What is Bytom?
Bytom is a blockchain protocol for financial and digital asset applications. Using the Bytom protocol, individuals and enterprises alike can register and exchange not just digital assets (i.e. Bitcoin) but traditional assets as well (i.e. securities, bonds, or even intelligence data).
The problem: Real world assets are becoming tokenized as we move ownership records and exchange ledgers to the blockchain. From a protocol level, though, there currently isn’t a unified way to map those assets from the physical to the digital world. Beyond mapping, there still needs to be some interoperability between the two asset forms as well to create one cohesive ecosystem. Until this happens, it’s hard to imagine a “tokenized” world. This is what Bytom is aiming to solve.
In this Bytom beginner’s guide, we’ll go over:
- How does Bytom work?
- Bytom team & progress
- Trading
- Where to buy BTM
- Where to store BTM
- Conclusion
- Additional Bytom resources
How does Bytom work?
Bytom’s mission is “to bridge the atomic [physical] world and the byte [digital] world, to build a decentralized network where various byte assets and atomic assets could be registered and exchanged.”
The three types of Bytom assets are:
- Income assets: These include non-performing assets, local government investments, and crowdfunding campaigns.
- Equity assets: This asset class requires investor verification for transfers and includes things like equity in private companies as well as shares of a non-public investment.
- Securitized assets: This type of asset has a predictable cash flow. Examples include debts and automobile loans.
You’re able to trade all of these assets on-chain with the Bytom protocol. And, this has a lot of benefits. Recording asset ownership and exchanges on the blockchain creates a more efficient and secure system than what’s currently available.
It removes the much of the bloat that middlemen create in asset transfers and record keeping. Removing the middlemen leads to lower costs and transfer times. This removal also has the added benefit of giving you full control of your assets. You no longer have to trust a third-party to keep accurate records because they’re stored on an immutable, public ledger. And, because the asset records are distributed worldwide across nodes, there’s not a single point of failure in which a malicious actor can manipulate the data.
The Bytom protocol also includes the capability for cross-chain transactions through side chains. To do this as a developer, you just create a smaller version of the chain and execute API calls through smart contracts to verify the network activity on that main chain. In doing this, the calls allow you to transfer assets between chains and even distribute dividends through the side chain too.
Bytom Token (BTM)
The Bytom Token (BTM) has three main uses in the Bytom ecosystem:
- Transaction fees
- Dividends
- Asset issuance deposits
There are currently 987 million BTM in circulation with a total supply of 2.1 billion that enter circulation through mining. The team distributed 30 percent of the supply to ICO participants and created a pool for mining rewards with 33 percent of the total supply. The remaining tokens are held in reserve, used for business development, or were given to private investors.
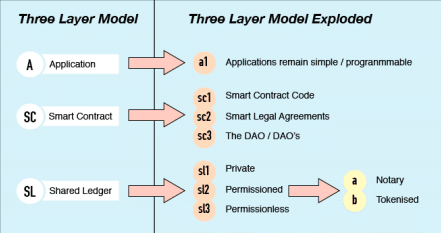
System Architecture
The Bytom architecture is separated into three layers: Application, Contract, and Ledger.
The Application Layer is what you interact with as an end-user. This includes the mobile and web apps that you work with in order to manage your assets. Interacting with this layer triggers contract calls on, you guessed it, the Contract Layer.
The Contract Layer contains two types of contracts. The first, the Genesis Contract, issues and audits other smart contracts on the network. More importantly, though, it ensures that all the assets using Bytom adhere to the standardization rules of the protocol.
The next, the General Contract, has two similar functions. The first function facilitates the trading of assets between protocol users. The second one sets up and verifies dividend distributions. In order to deploy a new asset through the General Contract, you first need to send it to the Genesis Contract for approval.
Lastly, the foundation of the Bytom protocol is the Ledger Layer. It’s here that Bytom connects to the blockchain. This blockchain is permissionless, public, and uses a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus algorithm. Unlike with some other PoW projects, you can use an ASIC to mine on the network, and the team even encourages it in their white paper.
Bytom team & progress
Headquartered in China, the Bytom team includes some heavy-hitters from the blockchain space. Founder Chang Jia left the world of Sci-Fi writing to create 8btc, one of the largest Bitcoin and blockchain news sites in China.
The other founding partner, Duan Xinxing, is the former Vice President of OKCoin, one of the largest digital asset exchanges in the world.
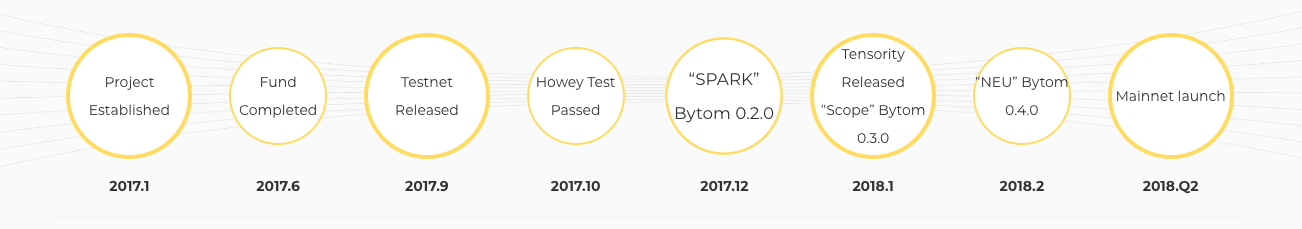
The project began in January 2017, and the team has been making steady progress ever since. They released their first testnet in September of that same year and launched the first version of the mainnet at the end of April this year. The project has also officially passed the Howey Test meaning that the SEC will not classify the token as a security.
There aren’t many other projects attempting to accomplish the same goals as Bytom. Ravencoin is another project (albeit much smaller currently) that wants to improve asset transfers. Unlike Bytom, Ravencoin is ASIC-resistant. You can also view projects that tokenize gaming assets, like WAX and Enjin Coin, as competitors. Although starting with the gaming industry, the project teams have plans to expand into other types of assets as well.
Trading
Bytom has had a turbulent trading path throughout its history. Other than a brief spike directly after the coin began trading in August, the price stayed relatively flat at around $0.08 (~0.000013 BTC) for most of 2017. The price saw a slight increase as the project passed the Howey Test in October 2017, but didn’t see significant growth until mid-December as it grew with the rest of the market.
Continuing to follow the overall market, the Bytom price fell sharply in January 2018 but has since recovered nicely. Towards the end of April, the BTM price reached an all-time high of $1.13 (~0.000124 BTC). However, it now sits at ~$0.71 (~0.000081 BTC).
As with most other projects, partnership announcements and additional adoption should cause the price to increase further.
Where to buy BTM
For a cryptocurrency with a market cap as large as BTM, you may be surprised to find out that it’s not listed on many of the major exchanges.
BTM is most commonly bought on RightBTC, a Dubai-based exchange, with BTC. You can also exchange USDT, BTC, or ETH for BTM on Huobi and Bibox.
For a complete list of exchanges and trading pairs for BTM, check out CoinMarketCap.
Where to store BTM
You should store your BTM in the Bytom official wallet. It’s available on Windows, Mac, and Linux operating systems. The team has also created a user manual to help you set-up and use the wallet.
As of this writing, Bytom is in the process of converting the ERC20 BTM tokens to the regular BTM tokens on the Bytom blockchain. If purchasing BTM now, make sure you contact the exchange to clarify which tokens you’re receiving. You should only send the regular BTM tokens to the official wallet.
Conclusion
Bytom is creating an interoperability protocol to enable the transfer and management of physical and digital assets. The team is led by some of the earliest blockchain evangelists, and they’ve been hitting key milestones since their founding in 2017.
If successful, we could see a new era of a tokenized world with digital assets representing anything from a company share to a plot of land. Although still early, the future looks promising based on the work the Bytom team has completed so far.
Additional Bytom resources
The post What is Bytom (BTM)? | Beginner’s Guide appeared first on CoinCentral.

Coincentral.com is author of this content, TheBitcoinNews.com is is not responsible for the content of external sites.
Our Social Networks: Facebook Instagram Pinterest Reddit Telegram Twitter Youtube











