What is Wanchain?
Wanchain is creating a new financial market of digital assets by implementing cross-chain transfers across different blockchains. With the number of various coins, tokens, and blockchains currently in the ecosystem, there’s not currently an efficient, decentralized way to exchange value between them. As an independent blockchain, Wanchain connects the accounts of independent chains to provide a framework to exchange these assets.
The platform isn’t just for currency transfers, though. Through smart contracts, privacy protection protocols, and the native Wancoin (WAN) token, among other things, you can use Wanchain to build a myriad of financial applications.
In this Wanchain beginner’s guide, we’re going to outline:
- How does Wanchain work?
- Wanchain team & progress
- Trading and where to buy WAN
- Where to store WAN
- Conclusion
- Additional Wanchain resources
How does Wanchain work?
Although forked from Ethereum, Wanchain is a completely separate blockchain, and its Wancoin (WAN) is not an ERC20 token. There are a lot of parts to the platform, but the cross-chain communication protocol is the backbone behind it all.
Cross-chain Communication Protocol
The cross-chain communication protocol provides a way to transfer data between Wanchain and other chains. The protocol has three functional modules:
- Registration module: Registers the chain that a transaction originates from as well as the asset that’s being transferred
- Cross-chain transaction data transmission module: Initiates the cross-chain transaction request to Wanchain, acknowledges whether the validator node returns success or not, and facilitates the legal transaction from the validator node to the original chain
- Transaction status query module: Monitors the status of the transaction
In essence, the cross-chain communication protocol utilizes smart contracts to enable you to exchange assets to Wanchain and vice versa.
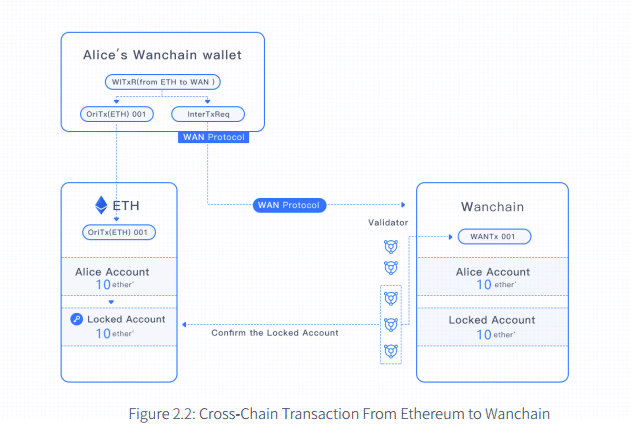
Verification Node Consensus Algorithm
Wanchain will follow Ethereum in its move to a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm. The platform will likely implement solutions like Plasma and the Raiden Network as well. Building on PoS, there are three types of verification nodes that maintain the overall network and split transaction fees:
- Vouchers: cross-chain transaction proof nodes
- Validators: general verification nodes
- Storemen: locked account management nodes
Vouchers receive a security deposit from the transaction fee. In return, they provide proof of the transaction between the original account and the Wanchain locked account. If this proof is false, the security deposit is taken from the holding account, and the Voucher will no longer be able to authorize transactions.
Validators record the transactional data on Wanchain’s blockchain in exchange for a portion of the transaction fee.
Storemen must stay online and maintain their own key shares (more on this below) to receive their portion of the fee.
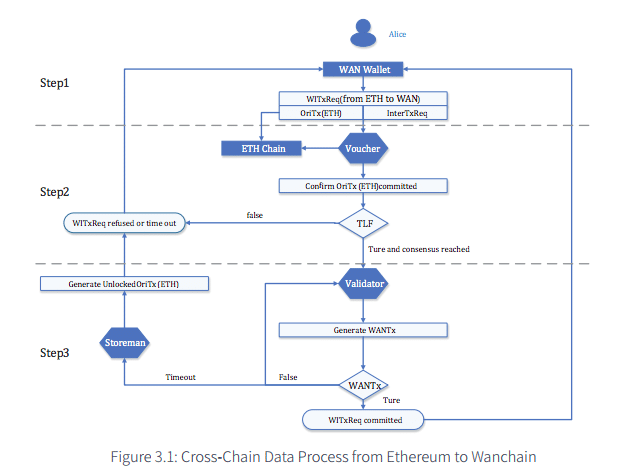
If you don’t hold enough Wancoin to run a verification node, you can still operate a general node. As a general node, you don’t directly validate transactions. Instead, you entrust your stake to a verification node who, in turn, distributes a portion of the transaction fees back to you.
Locked Account Generation Scheme
Wanchain uses the Locked Account Generation Scheme to secure funds and keys when there are multiple parties involved. Based on Shamir’s Secret Sharing Scheme, it effectively breaks up a key into shares and distributes it to all included participants.
The Storemen are responsible for maintaining and managing the appropriate key shares of the locked accounts for transactions.
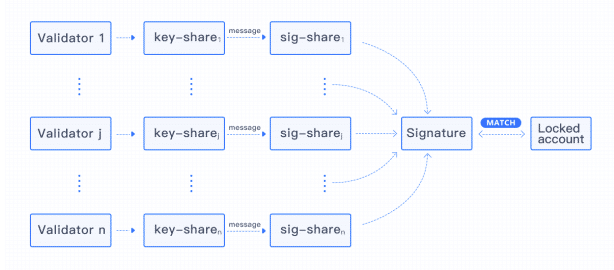
This method of key share distribution has a few benefits. Because Wanchain generates locked accounts through multi-party computations, there’s increased decentralization. And there’s more stability because you don’t need every key share to produce a signature for a locked account. If some of the Validators are offline, transactions can still be executed with a minimum number of shares.
Finally, any transaction with a locked account is done via the original chain. This means that any chain can easily integrate and interact with Wanchain without the need for new transaction types or validators.
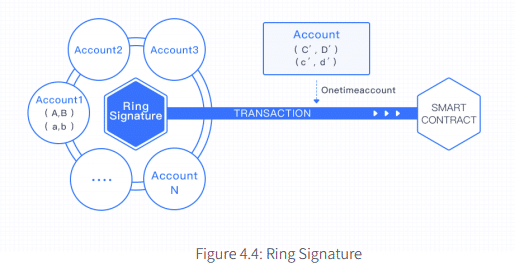
Smart Contract Token Transaction Anonymity
Wanchain is one of the first blockchain projects to include privacy within smart contracts. The platform uses ring signatures and one-time address generation to provide you with anonymity in your transactions.
In a ring signature, your signature as a sender is mixed with other fake accounts. This mixture makes it difficult to trace you as the actual sender. On top of that, Wanchain generates a new address for each transaction, so detecting transaction patterns is near impossible.
Wancoin (WAN)
Wancoin (WAN) is Wanchain’s native token. Transactions consume a certain amount of WAN, and you need to pay WAN security deposits to the cross-chain verification nodes when making transactions.
The team sold 107.1 million tokens during their ICO to raise a little over 120,000 ETH. These tokens comprise 51% of the supply. The team plans to use the ICO funds in the following way:
- 60% research and development
- 10% community development
- 10% marketing
- 10% infrastructure
- 10% daily operations
Wanchain team & progress
The Wanchain Foundation is a non-profit organization primarily operating out of Singapore but also has a significant presence in Austin, TX.
Wanchain was founded by Jack Lu, a respected player in the blockchain space. Before his current role, Lu co-founded Factom and started Wanglu Tech, a blockchain application development company. Wanglu Tech has been a primary contributor to the open-source Wanchain project.
Dustin Byington serves as the Wanchain President. Byington is a blockchain veteran having founded Bitcoin College in 2014 as well as co-founding Tendermint, a software mechanism to securely and consistently replicate applications across machines. Byington also co-founded Satoshi Talent, a platform to connect blockchain entrepreneurs with developers.
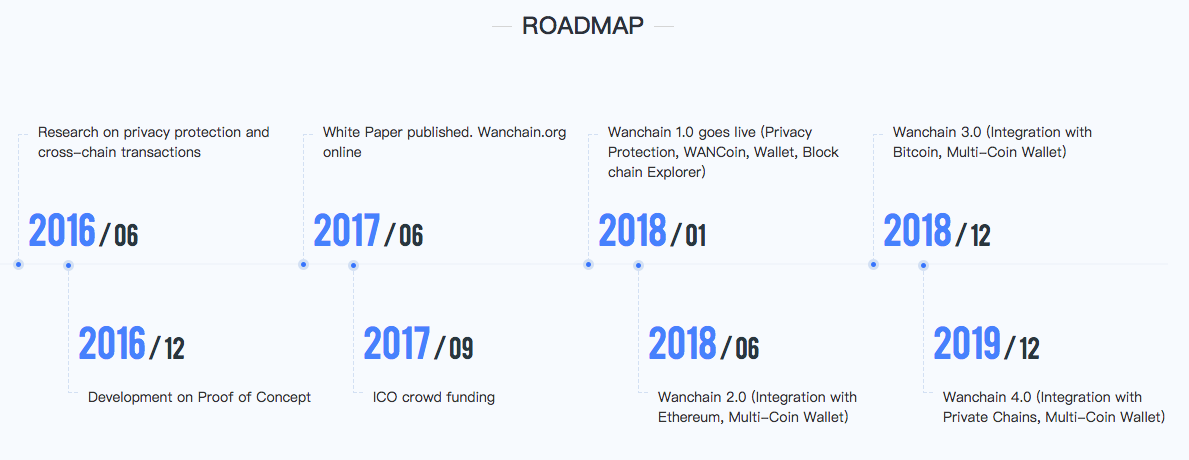
The team recently launched their main net and have an ambitious roadmap planned for 2018. The June 2.0 release will include Ethereum and Bitcoin cross-chain trading as well as a multi-currency wallet.
Because Wanchain is addressing the entire financial market, there are quite a few other projects that you can consider to be competitors. Ripple and Stellar, with their heavy involvement with financial institutions, may be the most comparable to the project.
Ark and its coinciding Smart Bridges are also working to connect the blockchains of different digital assets. And because you’re able to build decentralized applications using Wanchain, Ethereum could even be considered a competitor.
Wanchain is unique in that it combines the functionality of many other major projects to create an entire financial ecosystem. It’s also one of the few projects, if not the only one, to use ring-signatures and one-time addresses to provide anonymous smart contracts.
Trading and where to buy WAN
At the time of this writing, WAN has not started trading. Only ICO contributors have access to the coin. The project’s blockchain wasn’t available during the ICO, so instead the team distributed ERC20 tokens. With the recent launch of the main net, though, ICO participants can now trade in those ERC20 tokens for WAN here.
Be careful. The WAN ERC20 token that’s currently trading on EtherDelta has no value. Because trading the ERC20 token violates the ICO Terms of Service, you can’t exchange ones that have been traded for the new Wancoin.
Some things that may affect the WAN price down the road include further development updates, partnership announcements, and overall usage of the platform.
Where to store WAN
You should store your WAN in the Wanchain provided wallet. It’s available on Windows, Mac, and Linux operating systems. Although it only holds WAN now, it’ll soon support multiple currencies.
Conclusion
Wanchain is aiming to decentralize the financial industry through cross-chain smart contracts. With this technology, businesses can create blockchain applications for:
- Borrowing and lending
- Payments and settlements
- Transactions and exchanges
- Investment and financing
Plus, a handful of other financial services.
Although this is a challenging project, the team has a track record that should give investors confidence that they can pull it off. With the main net already in production, Wanchain is ahead of the majority of other blockchain projects. Hitting exchanges soon and V2 on the horizon, 2018 is shaping up to be a big year for the project.
Additional Wanchain resources
The post What is Wanchain? | Beginner’s Guide appeared first on CoinCentral.

TheBitcoinNews.com – Bitcoin News source since June 2011 –
Virtual currency is not legal tender, is not backed by the government, and accounts and value balances are not subject to consumer protections. TheBitcoinNews.com holds several Cryptocurrencies, and this information does NOT constitute investment advice or an offer to invest.
Everything on this website can be seen as Advertisment and most comes from Press Releases, TheBitcoinNews.com is is not responsible for any of the content of or from external sites and feeds. Sponsored posts are always flagged as this, guest posts, guest articles and PRs are most time but NOT always flagged as this. Expert opinions and Price predictions are not supported by us and comes up from 3th part websites.
Advertise with us : Advertise
Our Social Networks: Facebook Instagram Pinterest Reddit Telegram Twitter Youtube











