TRON Virtual Machine (TVM) was launched on July 30, 2018.
Previously, during the live streaming of TRON Independence Day, Justin Sun, the founder of TRON, revealed that TRON team was fully dedicated to updating the TVM. It is expected that the newest version of TVM will be launched on test.tronscan.net on July 30th.
People who are confused may ask, what is the “virtual machine”? What is the “blockchain virtual machine”? Despite that the EVM was already heard of, what is the TVM then?
First, with regard to virtual machine, Wikipedia gives the definition: in the architecture of computer science, it refers to a special kind of software that can create an environment between the computer platform and the end user, based on which the end user can operate the software.
Now you can get to understand TRON Virtual Machine (TVM) step by step through several problems:
What is a virtual machine?
What is a blockchain virtual machine?
What is the TRON Virtual Machine (TVM)?
Virtual Machine
First of all, to understand what a virtual machine is, you need to know the reason why a virtual machine is developed.
Assume that you are a programmer and have a PC with a Windows system installed. However, due to work requirements, you now need different operating systems to complete the work; meanwhile, the company has so limited funds that it is impossible to provide computer equipment with different operating systems. So what should you do now?
That’s the point when the virtual machine came into being.
Now a virtual machine is needed to create an environment for you to run any operating system.
Is it easier to understand the virtual machine in this way? Simply put, it is a software that creates an environment to allow users to operate other software in different environments.
With the virtual machine, users are able to, in the first place, run any operating system. So the original intention of the virtual machine is to simulate the environment so that different operating systems can be realized by one device.
Therefore, the virtual machine actually focuses on one thing – to simulate the environment.
Blockchain Virtual Machine
The virtual machine mentioned above means a complete computer system running in an isolated environment. However, this meaning has been diluted a lot in blockchain. Blockchain virtual machine, with the main function of running a smart contract, is essentially a code running environment.
To know the blockchain virtual machine, you first need to understand why the blockchain technology requires a virtual machine.
The evolution of the blockchain:
Blockchain 1.0, pioneered by Bitcoin. The blockchain technology at this time is mainly to provide simple technical support for different currency transactions.
Blockchain 2.0, symbolized by Ethereum’s developing smart contracts and Turing-complete EVM (a complete set of smart contract operating environment, with the official language as Solidity). Virtual machine has been gradually improved.
Blockchain 3.0, characterized by large-scale DApp landing applications. While large-scale landing testing requires the virtual machine to complete.
From the above evolution process, it can be inferred that the virtual machine plays an important role in the development of blockchain technology.
The blockchain technology developed from supporting currency trading in 1.0 era and DApp landing in 2.0 era to the large-scale DApp landing application in 3.0 era, thus indicating the continuous evolution of blockchain technology.
Nowadays, it has evolved to the 3.0 era. To achieve large-scale DApp landing application and ensure stable and safe operation, there is a crucial step: testing, i.e., creating an environment to test. At this point, we can see the development of blockchain technology both supports and desires virtual machine technology.
As shown above, the user sees and uses the developer’s DApp, a stable and secure product, directly on the public network. In order to ensure no problem exists, developers need to test the DApp on the virtual machine first and then run it on the public chain.
It can be indicated which role the blockchain virtual machine plays in the DApp landing application.
Currently, there are few projects that developed blockchain virtual machines with Turing completeness.
Since Ethereum developed the first Turing-complete virtual machine EVM, up-rising stars such as Qtum have also developed their own virtual machines. TRON is one of them.
The TVM is said to be fully compatible with the EVM and will be compatible with more mainstream VMs later. So, what makes TRON so ambitious?
Let’s take a look at the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
EVM is a code running environment built on the Ethereum blockchain, with the main function to handle smart contracts in the Ethereum system. To put it simply, it aims to provide an operating environment for all smart contracts developed through Ethereum.
Another phrase should be explained here, i.e., smart contract, which is usually inseparable from the blockchain virtual machine. Simply put, a smart contract is a program that runs on a blockchain.
Ethereum has created a system dedicated to the blockchain. In order to reduce resource consumption and ensure system performance, the EVM uses a more lightweight virtual chassis instead of a model that simulates a complete computer. Also introduced is the high-level programming language Solidity based on the Ethereum electronic distributed code contract.
However, there are many vulnerabilities in the EVM, for example, it only supports customized development languages so that some other programming languages cannot be ported.
As regards multi-language support and deployment of more smart contracts to the blockchain virtual machine, EVM is far from competent. Thereby a set of virtual machines that supports more languages is required.
TRON Virtual Machine (TVM)
With the above introduction, it is not difficult to understand the TVM is developed out of both the blockchain technology requirements and the need of its own development.
On June 25, 2018, TRON officially launched the mainnet and generated genesis blocks.
On July 30, 2018, the new version of TVM was launched.
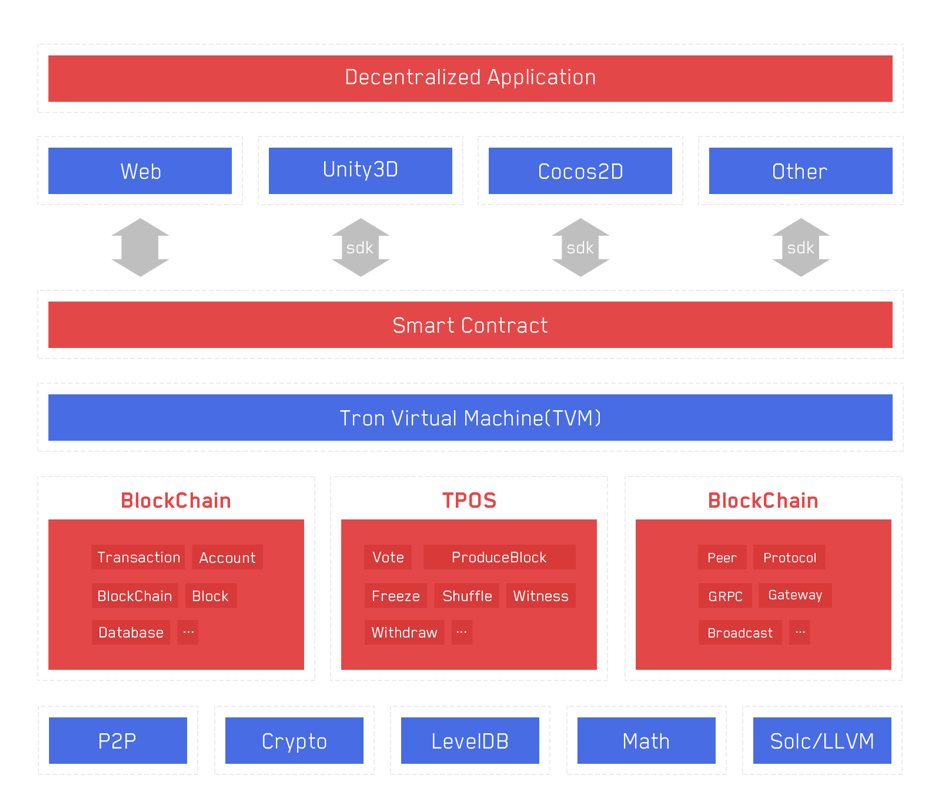
Workflow of a virtual machine previously published by TRON:
compilation of TRON smart contract —> execution and computation engine of virtual machine —-> external interoperability layer of virtual machine
So far, the TVM is mainly compatible with the Solidity language. The translator translates the smart contract into bytecode that TVM can recognize and execute. The data is processed in the virtual machine. Finally, access to the blockchain data is realized and the interface layer of the external data is invoked.
In the technical documentation TRON published before, we can see the core architecture is compatible with multiple languages.
The design concept of TVM is as follows:
And on the latest TVM announcement on July 30, it shows:
TRON implements a stacked virtual machine, uses an optimized instruction set, applies the Java language as the contract language, and subsequently adds more high-level language support, thus developers can better develop DApps.
So what is the significance and advantage of TVM compared with EVM?
First, to meet the requirement of self-development.
In order to occupy a place in blockchain 3.0, TRON needs to truly advance the technology, i.e., the large-scale DApp landing application can be put on TRON mainnet. In order to compile, debug and test to realize this, it is necessary for TRON to develop its own virtual machine. That is, due to TRON’s own development needs, TVM must be developed.
Second, to be compatible with EVM and even more VMs.
In the early days of development, TVM determined the goal of perfect compatibility with EVM, and in fact did it. In addition, it also promised to be compatible with more mainstream VMs in the future, thus owning the ability to meet diverse task scenarios innately and complete the scenario docking of more complex services in the future.
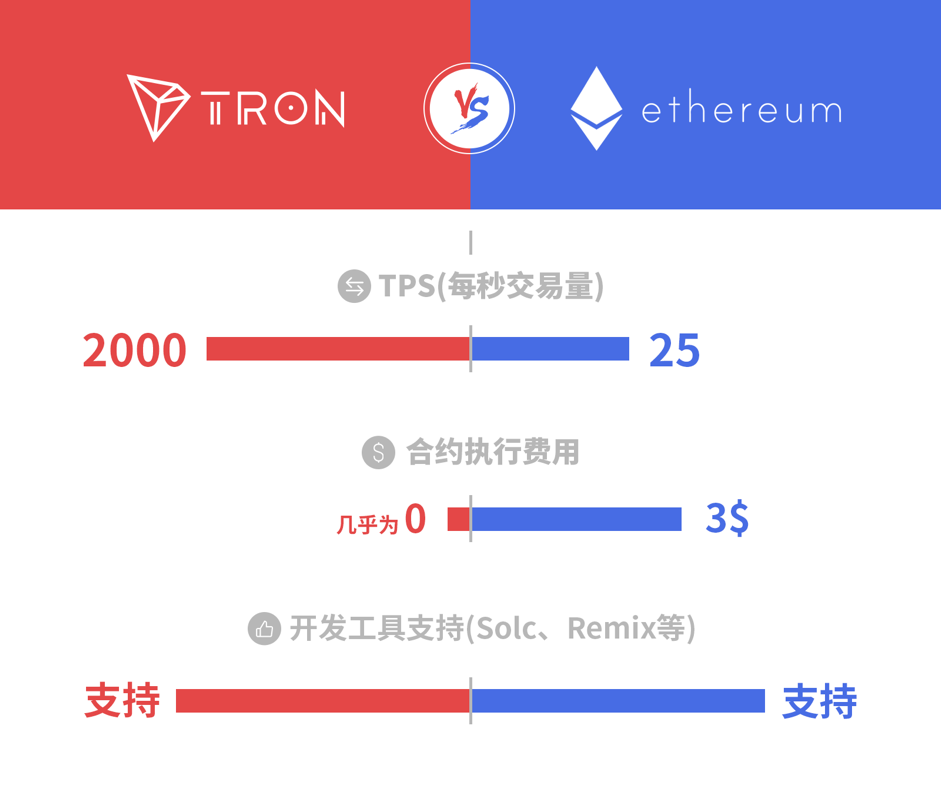
Third, to make up for the EVM.
Each transaction on Ethereum will be charged a certain amount of gas, which is intended to limit the amount of work required to execute the transaction and pay for the execution. The transfer and smart contract operations in the TRON system, however, are totally free, so the total amount of calculations that can be performed in TVM is not limited by the total amount of tokens in principle. Therefore, developers are allowed to focus more on the logic of the contract code and provided with a friendly one-stop interface for deploying, triggering, and viewing smart contracts.
In short, TRON is compatible with the existing Ethereum’s smart contract system, thus the contract scripts in Ethereum can be easily ported to TRON. According to the plan, TRON will be compatible with EOS’s smart contract system in the next step and more in the future.
It can be seen that the ambition of TRON is quite great, and Justin Sun is also quite smart, for he is able to identify the opportunities and pain points of the entire blockchain industry in the current stage.
Disclaimer: This article should not be taken as, and is not intended to provide, investment advice. Global Coin Report and/or its affiliates, employees, writers, and subcontractors are cryptocurrency investors and from time to time may or may not have holdings in some of the coins or tokens they cover. Please conduct your own thorough research before investing in any cryptocurrency and read our full disclaimer.
Image courtesy of Pexels
The post TVM was launched after TRON mainnet appeared first on Global Coin Report.
Read more at https://globalcoinreport.com/tvm-was-launched-after-tron-mainnet/

Globalcoinreport.com/ is author of this content, TheBitcoinNews.com is is not responsible for the content of external sites.
Our Social Networks: Facebook Instagram Pinterest Reddit Telegram Twitter Youtube