What Is IOTA?
IOTA stands for Internet of Things Application, and it’s a crypto technology that facilitates transactions between devices on the Internet of Things (IoT). IOTA addresses the transaction fees and scalability issues of blockchain technologies by getting rid of the block and chain. Instead, in order to submit a transaction to the IOTA ledger, you must verify two other previous transactions.
This method of verification means there’s no central ledger, and there’s no need for miners to power the network.
As the devices on the network randomly verify each other’s transactions, they build consensus through the web of connections between transactions. In cryptography, this type of verification is known as Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG), but the creators of IOTA call it the Tangle.
Since computing power in the Tangle grows as the network grows, IOTA is promising free, fast transactions. It’s also designed to process micro-payments and payments between machines, facilitating a whole machine-to-machine micro-economy.
While IOTA makes big promises, the technology is still new, and it’s not without its detractors. In this article, we’ll look at:
- How Does IOTA Work?
- Team & Progress
- Concerns, Weaknesses, & Critiques
- Trading
- Where to Buy IOTA
- Where to Store IOTA
- Conclusion
- Additional Resources
Technical Details
- Launched: June 11, 2016
- Total coin supply: 2,779,530,283,277,761
- Algorithm: Proof of Work (PoW) using a version of SHA-3
- Block time/reward: No blocks, verify two transactions to submit your own transaction
How Does IOTA Work?
The Internet of Things is already a major force in the world economy.
Companies are creating cameras, sensors, and other devices to monitor conditions in factories, shipping lanes, farms, stores, and homes. According to research from Gartner, IoT grew to 8.4 billion devices in 2017, and the outlook for future growth is exponential.
IOTA’s vision is to be the platform for machine-to-machine (M2M) transactions. IOTA’s founders started the company after working in the IoT industry, and they argue that in order for IoT to be most useful, the devices in the network need to share and allocate resources efficiently.
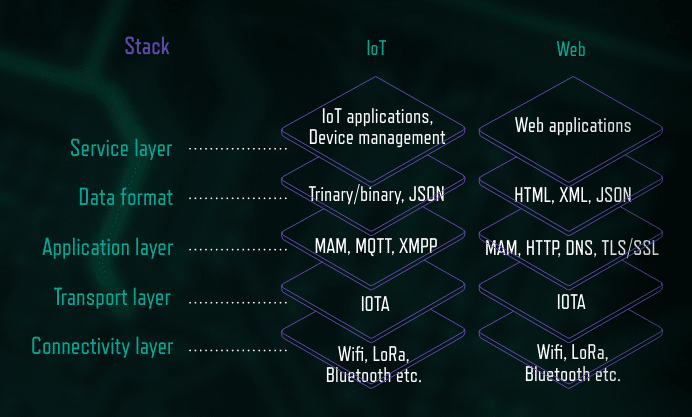
Where IOTA Fits in the IoT and Web Technology Stacks
This means the devices need to be able to purchase more electricity, bandwidth, storage, or data when they need it, and sell those resources when they don’t need them.
Even on a small network, this means potentially dozens of transactions per second as devices communicate and use resources. With so many transactions, at such a small, fast scale, IOTA’s founders believe blockchain technology isn’t adequate for IoT applications.
Blockchain networks struggle with scalability, and they often resort to charging fees in order for miners to include your transaction in a block sooner. IOTA aims to solve both scalability and fees with its new network so that billions of IoT devices can use it.
Scalability: IOTA Is Not a Blockchain Technology
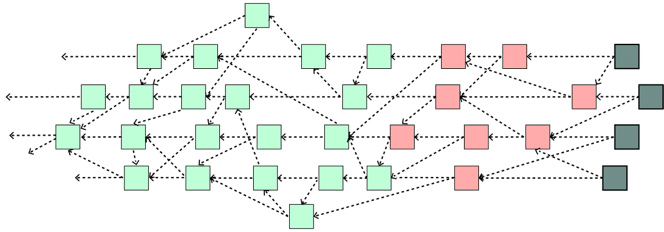
Graphic Representation of the IOTA Tangle
Since IOTA plans to have billions of transacting nodes on its network once fully implemented, the founders needed to design a network where the processing power grows as nodes on the network grow. To that end, they designed The Tangle, a consensus-building system where the device submitting a new transaction must first verify two other transactions on the network. For each verification, the verifier performs a small proof of work linking the transactions into the overall Tangle.
The Tangle means that consensus is reached based on a web of verifications. Each transaction is linked to the two transactions it verified. And over time, it will be linked to future transactions that verify it. This solves the scalability problem as the network no longer relies on a central blockchain.
Every new device on the network contributes its computing power to the network when it submits a transaction. The Tangle also eliminates block mining, and all the coins on IOTA were created at the genesis of the network.
Transaction Fees: How IOTA is Free to Use
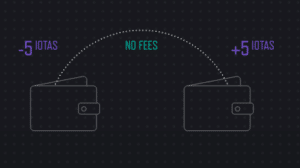
Since you contribute computing power to the network when you submit a transaction, the cost of using the network is only as great as the electricity needed to verify two other transactions. The Tangle allows IOTA to operate fee-free, and it means the network is even more distributed than a blockchain network. With blockchain, the network is distributed among the miners on the blockchain. With the Tangle, the network is distributed among every participating node.
The absence of fees is critical to IOTA’s mission of servicing IoT devices. These devices will often be transacting at fractions of a penny with high frequency. Any fees charged on such small transactions would make micropayments unfeasible. In order to serve as the backbone for the M2M economy, IOTA has to be free to use.
34% Attacks & The Coordinator
Those familiar with blockchain technology know that a blockchain is vulnerable if one party has 51% of the computing power on the network. At that point, it’s theoretically possible for a bad actor to create and verify false transactions. Since IOTA uses the Tangle to verify its transactions, it’s theoretically vulnerable if one party controls only 34% (greater than 1/3) of the network’s computing power.
You shouldn’t underestimate the difficulty of implementing a 34% attack against the IOTA Tangle. Since the Tangle is a complicated web of nodes and transactions, you’d still have to discover the nest of the network before you could leverage your 34% advantage.
IOTA is most vulnerable to such an attack early in its implementation (i.e. now). Since the early network is small, with fewer nodes, it’s easier for an attacker to accumulate a 34% share of the network. To combat this threat, the network is using a Coordinator in its early implementation to ensure the early Tangle isn’t compromised.
While it’s a necessary step for security early on, and IOTA plans to eliminate the Coordinator once the network is strong enough, it does mean that the platform and currency are currently centralized. And, you have to trust the IOTA Foundation if you decide to invest.
Proprietary Technologies
The IOTA team has received praise and criticism for its use of new technologies in developing the platform. Originally, IOTA used its own hash function known as Curl for all proof of work and key generation. While the proof of work hashing has since changed to a more traditional SHA-3 protocol, IOTA still uses the proprietary Curl hashing function for other applications on the platform.
IOTA also implements trinary logic, instead of binary. Using processors with three states could mean advantages in efficiency and overall computing power. The team is working closely with JINN Labs on hardware for IoT devices that are capable of computing in trinary.
Team & Progress
Launched via crowdsale in 2015, the network is now developed and supported by the IOTA Foundation, a German non-profit. David Sønstebø and Dominik Schiener lead the foundation as co-chairman of the board of directors. The rest of the leadership team includes the founder of Nxt, Volkswagon Chief Digital Officer, Fujitsu Head of Central Europe, and several experts across a wide variety of industries.
The 50+ member team has been making steady progress since the platform’s launch. One of the most important releases in the past year was that of the Data Marketplace at the end of 2017. The marketplace uses IOTA’s technology to facilitate the storing and selling of data streams. It already has several notable companies, such as Accenture and Bosch, participating on the network.
The team has also recently begun working on smart city technology for Europe and other parts of the world. This technology will include such things as biometric palm readings tied to digital identities as well as the combination of city IoT devices with the Tangle.
Competition
As far as cryptocurrencies targeting M2M payments, IOTA seems to be on its own. Projects like Waltonchain and Vechain tie in with IoT devices as well but have a focus on the supply chain industry. Although supply chain is one of IOTA’s verticals, it sits alongside three other ones – automotive, eHealth, and smart energy.
Because IOTA is a DAG-based crypto, you could say it’s competing with Nano and Byteball. However, neither of these competitors is focusing on the IoT sector. The teams of both projects have designed them more for peer-to-peer payments rather than payments between machines.
Concerns, Weaknesses, & Critiques
A number of crypto technology experts have questioned IOTA’s viability as a platform. Implementing so many new technologies at once, it’s difficult to believe that there are no weaknesses or flaws in its implementation. The technology behind IOTA simply hasn’t been tested enough to know how it will work at scale, and how it will hold up to attacks. This overall lack of testing and peer review is the biggest concern for IOTA’s detractors.
Last year, MIT and Boston University made waves when they published a scathing paper outlining critical security flaws in the Curl hashing function. The idea that you can “roll your own crypto” is strongly looked down upon in the community and among experts. Good cryptography takes years to develop, test, and review. The SHA-3 hashing algorithm took nine years to complete, and experts have shown concern that IOTA’s developers chose to try to write their own cryptography instead of using established standards.
It’s easy to forget, however, that every new technology goes through technical hurdles and growing pains. Bitcoin had the Mt. Gox scandal, and Ethereum weathered the DAO hack. While the technology and implementation behind IOTA will certainly change, you should consider the overall architecture of the IOTA cryptocurrency and the history of the development team when considering whether to invest.
Trading
IOTA trading has been turbulent, to say the least. The coin experienced its first significant run-up in August 2017 before slowly falling into the start of November. An increased interest from the community due to its partnership announcements with Refunite, UC Berkeley, and Norwegian healthcare organizations most likely caused the increase in price.
Following the September-November cooldown period, the IOTA price went parabolic. It reached an all-time high of $5.23 (~0.00031 BTC) in December 2017 but sharply fell with the rest of the market at the start of 2018. After a brief resurgence in April 2018, the price has continued to fall but has seemingly bottomed out at about $0.45 (~0.00007 BTC).
The aforementioned controversy has caused the IOTA price to fluctuate more wildly than other cryptocurrencies in this already volatile sector. Further demonstrations of the network’s security and stability should help bring investor confidence back to the coin. Additionally, the continued growth of the IOTA ecosystem through enterprise partnerships and general use will have a positive effect on the price.
Where to Buy IOTA
If you’re interested in buying IOTA, Bitfinex and Binance are your best options. While Bitfinex has the largest amount of trading volume, it’s not available to United States citizens. So, if you’re in the U.S., you should check out Binance instead.
Not sure on how to start? We’ve got you covered with our guide on how to buy IOTA.
Where to Store IOTA
There are two wallet options to consider for your IOTA storage: the official desktop GUI and the Trinity wallet.
The desktop GUI is what the IOTA team recommends you use to safely store your funds. The GUI wallet is available on Windows, Mac, and Linux devices. Using this wallet, you have the option on whether to access it as a light node or a full node. If you plan on just using the wallet for storage and transactions, a light node will suffice.
The Trinity wallet is simpler to use than the GUI. However, it’s currently in beta, so you may encounter some bugs. No matter which device you’re interested in using the wallet on, you should be in luck. It’s available on Windows, Mac, and Linux operating systems as well as iOS and Android devices.
Mobile Trinity Wallet
Conclusion
The IOTA cryptocurrency uses technology that has a lot of potential.
If successful, the Tangle could be a viable competitor to blockchain technology for transactions, and the IoT market for microtransactions will only continue to grow. Since IOTA is cutting edge, however, its technology remains largely untested. In the end, your decision to buy the coin should be based on thorough research about the technology and its founders. IOTA’s Tangle could be the next big advance in cryptography, but investing in an untested technology is inherently risky, so do your research.
Editor’s Note: This article was updated by Steven Buchko on 10.29.2018 to reflect the recent changes of the project.
Additional Resources
The post What Is IOTA (MIOTA)? | A Complete Guide to the IoT Cryptocurrency appeared first on CoinCentral.

Coincentral.com is author of this content, TheBitcoinNews.com is is not responsible for the content of external sites.
Our Social Networks: Facebook Instagram Pinterest Reddit Telegram Twitter Youtube