What Is a Blockchain?
A Blockchain is a decentralized database or digital ledger of cryptocurrency transactions that can be seen by all parties on the network.
The most recent transactions are recorded and added to form completed blocks in chronological order, allowing market participants to keep tabs on cryptocurrency-related transactions without central recordkeeping. Each computer connected to the network receives a copy of the blockchain, which is downloaded automatically.
The first blockchain to ever exist was created in 2009 by Satoshi Nakamoto, for the purpose of sending payments digitally and anonymously between two parties without needing a middleman to verify the transaction.
How Does Blockchain Work?
 Blockchains are basically shared databases that contain entries that require to be confirmed and encrypted.
Blockchains are basically shared databases that contain entries that require to be confirmed and encrypted.
A block is the newest and developing part of a blockchain. It records recent transactions until it is completed. Afterward, the block goes into the blockchain as a permanent database and a new block is generated. All the blocks in the blockchain are connected in linear and chronological order. Each block has the hash of the previous block. The blockchain contains information about the addresses and balances of various users, starting from the genesis block to the last block to be completed.
Blockchains are immutable, meaning that when new data is entered, it can never be erased. Even though the data cannot be erased, consenting parties can update the blockchain and the data can be distributed, but not copied.
The size of a blockchain grows by each cryptographic add of a block and is thought by some to create problems in storage and synchronization.
The code and framework behind blockchains can be a secure, digital alternative to banking services, and a useful tool in financial processes.
But, in spite of its great potential, blockchain technology is still in a growing phase; as a result, setbacks in technology deployment and bugging issues can occur.
Consensus protocol
The most defining feature of a blockchain is its consensus protocol, which makes sure that all network participants follow the network’s rules. The two most common consensus protocols are the Proof of Work (PoW) algorithm or Proof of Stake (PoS) algorithm.
For blockchains that issue cryptos, the consensus dictates how new coins are released from the blocks. With PoW, new crypto is created through mining, a complex computational process, and with PoS, new crypto is given to network users by staking them in their wallets.
Distributed Computation
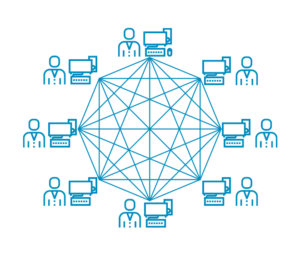 Blockchain has a resilient distributed architecture. Each user of a certain blockchain that runs a full node on his computer has to first download a copy of the entire blockchain. After this, the node can run independently and validate new transactions throughout the network.
Blockchain has a resilient distributed architecture. Each user of a certain blockchain that runs a full node on his computer has to first download a copy of the entire blockchain. After this, the node can run independently and validate new transactions throughout the network.
Nodes keep the transaction data in a block and help validate the proof-of-work for the block. An essential concept of the blockchain is the lack of a central node that processes and distributes the data, which ensures that the network will not collapse if one node ceases to work.
Types of Blockchains:
- Public Blockchains (permissionless ledgers) have no restrictions and enable anyone to contribute to the ledger;
- Private Blockchains (permissioned ledgers) are restricted only to participants that are invited by the creators of the network;
- Hybrid Blockchains (consortium blockchains) have both public and private blockchain characteristics. Hybrid blockchains have a set of rules, but the network is administered by a group of agreed-upon organizations instead of a single entity.
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchains
The first decentralized cryptocurrency ever created, Bitcoin, was born by making use of blockchain technology. Since its apparition, thousands of cryptocurrencies have been created by using the same blockchain technology and cryptography, thus facilitating secure and anonymous transactions.
Other Uses
 Currency is not the only application that can be built on blockchains. The Ethereum public blockchain platform has made use of this technology, and it uses it to make “smart contracts”. These contracts are digital contracts that bypass intermediary services, and it can be used to exchange money, property and shares in a transparent and conflict-free way. Smart contracts are scripts that self-execute when a certain set of conditions are met. Read more about them from What Are Smart Contracts?
Currency is not the only application that can be built on blockchains. The Ethereum public blockchain platform has made use of this technology, and it uses it to make “smart contracts”. These contracts are digital contracts that bypass intermediary services, and it can be used to exchange money, property and shares in a transparent and conflict-free way. Smart contracts are scripts that self-execute when a certain set of conditions are met. Read more about them from What Are Smart Contracts?
The technology is attracting not only financial institutions and stock exchanges but also people from the music industry, insurance, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. It has been suggested that it can be used for voting, weapon and vehicle registrations, medical records, as well as to confirm ownership of various artwork.
Given its potential to simplify business operations, new blockchain-based models have started to replace the inefficient accounting and expensive payments in the financial sector.
Hesitant at first, banks have started researching how they can install back-office settlement systems for trade processing, transfers, and other transactions at a higher rate, while also saving them money.
Security
 According to the CEO and founder of Northwest Passage Ventures, a firm that invests in blockchain technology companies, blockchain’s simple design makes it the most secure of technologies.
According to the CEO and founder of Northwest Passage Ventures, a firm that invests in blockchain technology companies, blockchain’s simple design makes it the most secure of technologies.
He goes on saying that: “In order to move anything of value over any kind of blockchain, the network [of nodes] must first agree that transaction is valid, which means no single entity can go in and say one way or the other whether or not a transaction happened. To hack it, you wouldn’t just have to hack one system like in a bank…, you’d have to hack every single computer on that network, which is fighting against you doing that.”
Co-founder of Netscape and co-founder and general partner of Silicon Valley venture capital firm Andreessen Horowitz, Marc Andreessen, also praised blockchain technology for its ability to securely move information in digital format:
“The practical consequence […is…] for the first time, a way for one Internet user to transfer a unique piece of digital property to another Internet user, such that the transfer is guaranteed to be safe and secure, everyone knows that the transfer has taken place, and nobody can challenge the legitimacy of the transfer. The consequences of this breakthrough are hard to overstate.”
No matter how secure it may be, we must keep in mind that no existent system is immune to hacking.
Computing resources are enormously high because technology needs lots of computers to find transactions and make or discover the blocks. To give things a perspective, the Bitcoin blockchain amasses a computing power varying from 10 to 100 times much more than all of Google’s combined serving farms.
“So again, [it’s] not un-hackable, but significantly better than anything we’ve come up with today,” – Tapscott.
Advantages
 Distributed ledger technologies have proven to be very efficient in cost savings. This system facilitates the internal flow of operations in the business and banking sector, significantly decreasing the number of expenses, mistakes, and delays, which usually occurred when dealing with traditional methods of record stocking.
Distributed ledger technologies have proven to be very efficient in cost savings. This system facilitates the internal flow of operations in the business and banking sector, significantly decreasing the number of expenses, mistakes, and delays, which usually occurred when dealing with traditional methods of record stocking.
Distributed ledger technologies will have the most impact in the following three areas:
Accounting
Accounting systems are more expensive to maintain in comparison to electronic ledgers, and it also reduces the number of staff.
Errors
Distributed ledger technologies eliminate repetitive confirmation steps and have far fewer errors due to the fact that the system is almost fully automated.
Processing
Less capital will be held in pending transactions if the processing delay is minimized.
DLT also saves brokers from putting more money into unsettled trades. The technologies’ transparency makes it easier to be audited and save money in anti-money laundering regulatory compliance costs.
Removing almost all human involvement will prove beneficial in cross-border trading, saving time because it is not affected by time-zone and the processing of all of the parties’ confirmations on their payment.
More Uses
Verify authenticity
Blockchain technology can enable people to verify the authenticity and origin of their products, as the information recorded on the ledger cannot be tampered with and is completely transparent.
US-based Verisart created a blockchain system for the auction market, called P8Pass, that records the details of artworks on the Bitcoin Blockchain. The company offers galleries blockchain-enabled certificates that prove the authenticity of artworks.
Fast money transfers
 Cross-border payments always have long processing times. Blockchain technology comes as a perfect solution in this scenario, as many banks and payment processors, have recognized its potential. The Ripple Network comprises hundreds of top banks and payment services that are using or will start implementing blockchain-based technologies that facilitate faster transfers. MoneyGram even started using the XRP token for its transactions quite recently.
Cross-border payments always have long processing times. Blockchain technology comes as a perfect solution in this scenario, as many banks and payment processors, have recognized its potential. The Ripple Network comprises hundreds of top banks and payment services that are using or will start implementing blockchain-based technologies that facilitate faster transfers. MoneyGram even started using the XRP token for its transactions quite recently.
Tech giant IBM created a banking solution for cross-border transactions, also based on Blockchain.
Issues
Even though there is a big hype now with blockchains, the technology is still new, and there are many strides to be taken before we can fully use it to its full potential.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology offers a lot of benefits, and the means to create flexible and secure businesses and operations. It remains to be seen if companies will succeed in adopting this technology and produce services and items which will interest customers. So far, the demand for blockchain-based services is rising, and the technology is evolving at impressive rates. It will also have a massive impact on the global economy, mainly thanks to a continuously growing list of real-world applications. But it will take time for people to develop and master the many uses of this technology.
Blockchain technology has endless potential applications. At the time being, some of the said applications are still in developmental stages or in beta mode. More and more investors are pouring money into blockchain startups, so it will not come as a surprise if distributed ledger services will become mainstream products in a few years.
Featured image: innominds.com

coindoo.com is author of this content, TheBitcoinNews.com is is not responsible for the content of external sites.
Our Social Networks: Facebook Instagram Pinterest Reddit Telegram Twitter Youtube